Yield refers to the income an investor earns from an investment, expressed as a percentage of its current price or face value. In fixed income, yield typically comes from the interest (coupon) payments on bonds and may also reflect gains or losses if the bond is bought at a discount or premium. Yield is a key measure for evaluating the attractiveness and potential return of fixed income investments.
Key characteristics
Types of yield: Common measures include current yield (coupon divided by current price) and yield to maturity (total expected return if held to maturity, including coupons and price changes).
Income gauge: Yield provides a snapshot of the income investors can expect relative to the bond’s price.
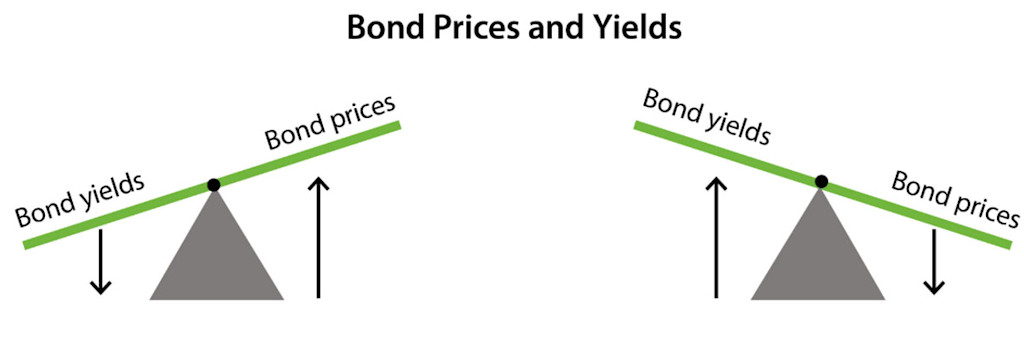
Price relationship: Yields and bond prices move inversely, this means when bond prices fall, yields rise, and vice versa.
Why yield is important
Comparing opportunities: Yield helps investors compare fixed income securities and select those that best meet their income and return goals.
Managing risk and return: Yield reflects the level of risk taken—higher yields typically compensate for higher credit or interest rate risk.
Generating income: Yield is a primary driver of the regular cash flows that fixed income investments provide, supporting income-focused strategies.
Signaling market conditions: Yield levels across maturities and sectors can provide insights into market expectations, economic conditions, and investor sentiment.
Yield plays a vital role in helping investors make informed decisions, balance their portfolios, and meet their investment objectives.




















