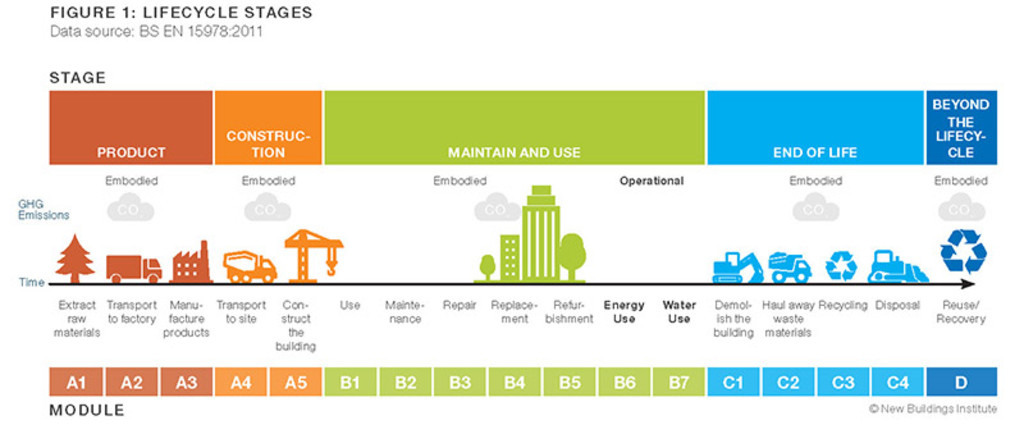
In the property sector, embodied carbon refers to the carbon emissions associated with the production and transportation of building materials and components, as well as the construction of a building, end-of-life (demolition, site clearance and disposal of material), ongoing physical maintenance and refurbishments.
Embodied carbon is only one element of a building’s whole life carbon footprint. The other being operational carbon which refers to the carbon emissions associated with the day-to-day energy use of a building, such as heating, cooling, and lighting.
Embodied carbon is more difficult to measure than operational carbon but as tools to measure it become more sophisticated it is expected to be recognized as an increasingly significant constituent of the property sector’s overall carbon footprint.
Green leases
Green leases are lease agreements with the objective of making the occupancy of a property sustainable. There is currently no common global standard that defines a green lease.
Typically a green lease incorporates clauses obliging owner and the lessor to undertake actions and maintain standards with regards to subjects including energy efficiency measures, waste management or disposal, and resource-use efficiency.
Green leases can help companies satisfy broader operational environmental obligations, save costs and satisfy, or futureproof against, regulatory requirements in the specific geography or jurisdiction, especially those related to energy efficiency.
Green lease clauses are expected to become a standard element of commercial property leases as environmental regulations governing the real estate sector become stricter.






















