Redesign inputs Redesign inputs
Consumer Packaging
Renewable Feedstock & Fiber
Building Materials
Precision Farming
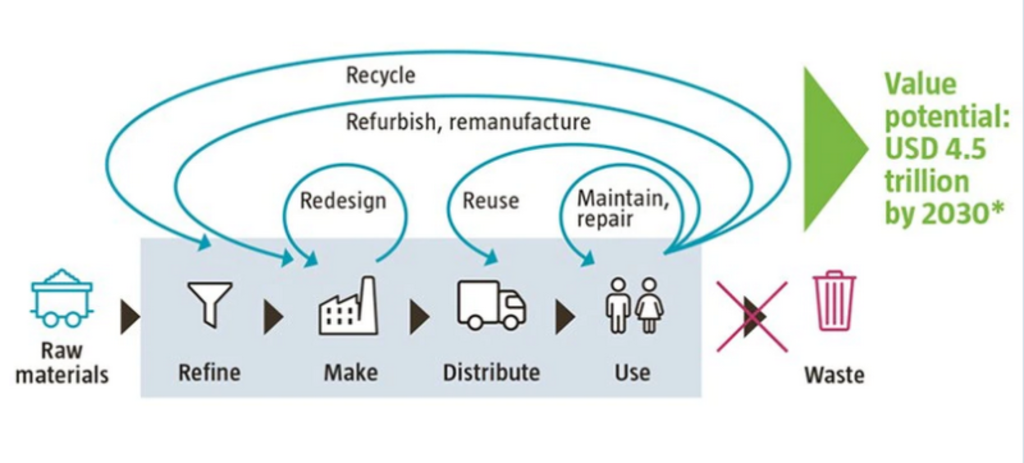
Much of the concept of the circular economy involves words beginning with ‘re-‘: recycling, redesigning, reusing, refining, refurbishing and repairing – to name the most common descriptors. This has two main objectives:
Making more efficient use of the Earth’s resources, as research shows that the linear model consumes finite resources at 1.75 times the planet’s annual regenerative capacity. In some areas such as farming and mining, we are already approaching planetary boundaries regarding deforestation, biodiversity and extractive limits.
Eliminating the billions of tons of waste that are produced by the linear economy every year, much of which ends up in unsustainable landfill, or is dumped in the ocean. Plastic packaging is a particular problem, since 80% of it is never recycled. Electronic devices are also commonly discarded, when it would be possible to retain up to 90% of the product’s value by using a more modular and recyclable design.
Source: Robeco
Rather than downsizing the economic model, proponents of the circular economy predict it will create USD 4.5 trillion in market opportunities by 2030 – principally through new means of production, recycling and sharing. New technologies such as developing biodegradable plastics, as well as changing consumer preferences regarding longer lasting products, are seen as major drivers.
In order to capitalize on this trend, Robeco founded its Circular Economy Equities strategy in January 2020 to target those companies that are contributing towards this concept. It does so through four clusters: redesigning inputs, enabling technologies, implementing circular use, and looping resources, as shown in the graphic below:


Consumer Packaging
Renewable Feedstock & Fiber
Building Materials
Precision Farming

Digitization
Product as Service
Logistic & Testing

Nutrition
Fashion & Leisure
Household & Lifestyle
Sharing Economy

Lifetime Extension
Collection & Sorting
Recovery & Recycling
The move towards a circular economy is becoming more urgent as increasing urbanization, a rising hyper-consuming middle class and a global population approaching 10 billion, create unsustainable pressure on resources and waste management. According to the European Union’s Circularity Gap Report 2020, only 9% of the current world economy is circular.