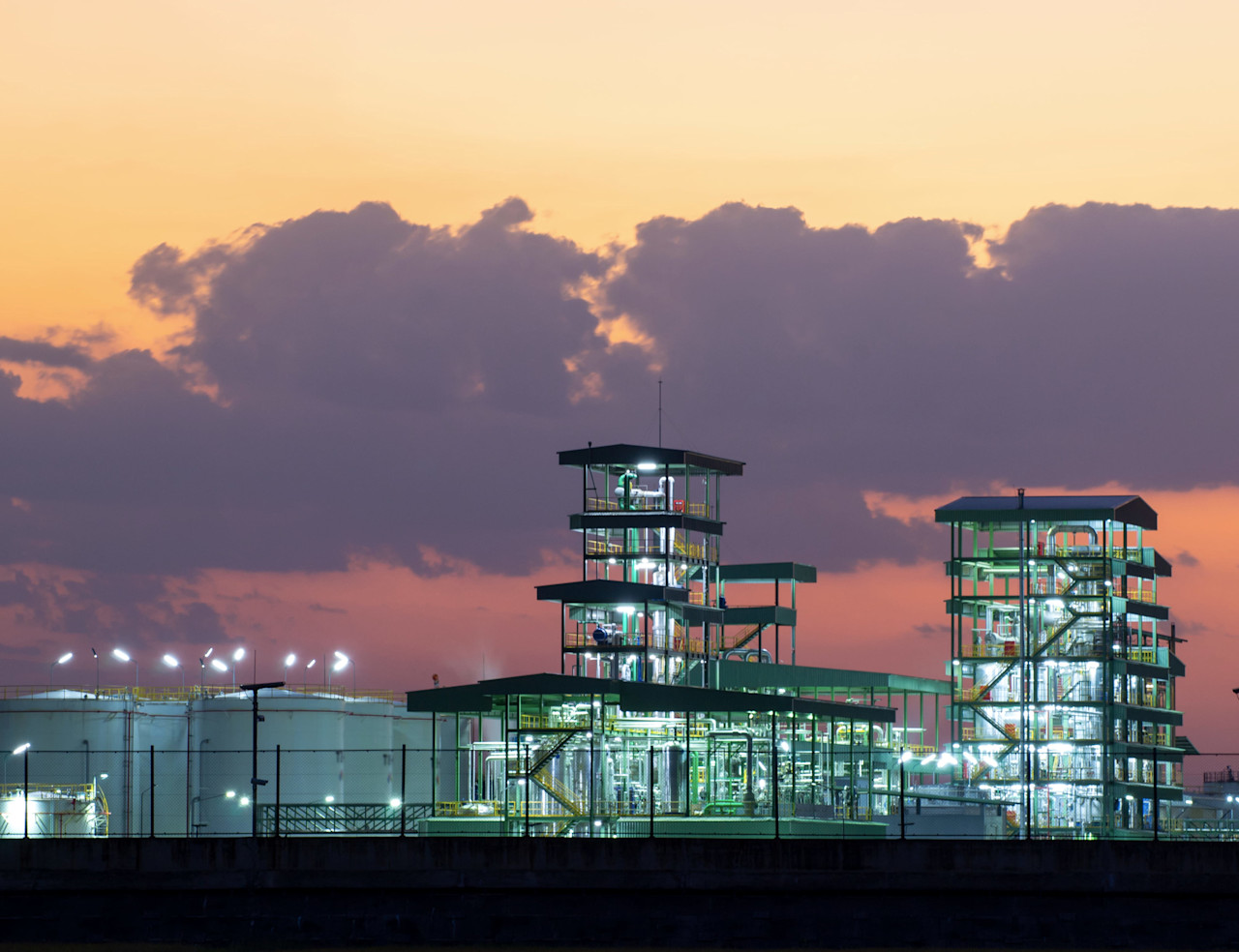
The triple bottom line embraces the notion of focusing on ‘people, planet, profit’ when making business and investment decisions, and not just on the profit motive. The term was first introduced to expand the traditional definition of a ‘bottom line’, which is the net profit made by a company after all its costs have been accounted for. It is also known as the ‘three Ps’ and provided an early framework for sustainable investing.
The triple bottom line: people, planet, profit
The phrase was coined in 1994 by British businessman John Elkington, who wanted enterprises to recognize that social and environmental factors were equally important for the long-term success of society. Elkington was the founder of SustainAbility, a think tank consultancy that promoted the adoption of economic, social and environmental sustainability by UK companies. He went on to become a best-selling author on corporate responsibility.

Creating returns that benefit the world we live in
Climate change
The idea of focusing on a triple rather than a singular bottom line emanated from a growing consciousness in the 1980s and early 1990s about the effects that a company’s operations can have on wider society. A mining company, for example, could make a handsome profit from extracting minerals, enjoying a strong bottom line. Yet, it’s operations could also have significant impacts on the environment and could be harmful to people in the event of an accident or pollution spill.
This concept also came to be applied to the tobacco industry, whose products posed a serious danger to human health and created environmental pollution through exhaled smoke. Conversely, other industries were able to make positive contributions to society, such as those building houses for lower-income groups. For these industries, the profit motive was a secondary factor. This is how the notion of incorporating all factors, such as people and the planet, began to take root.
The triple bottom line concept later morphed into the use of ‘environmental, social and governance’ factors, or ESG, which now forms the bedrock of most sustainable investing processes.